Ultimate Guide to Commercial Reverse Osmosis Systems 2026
This authoritative guide explores commercial reverse osmosis systems for 2026, covering working principles, cost analysis, maintenance protocols, and industrial applications. It addresses key questions on fluoride and microplastic removal, ensuring businesses make informed water treatment decisions.
- Introduction: The Critical Role of Pure Water in Commercial Operations
- What is a Commercial Reverse Osmosis System?
- The Science of Separation
- Commercial vs. Residential Distinction
- How Commercial Reverse Osmosis Systems Work: A Deep Dive
- 1. Pre-Treatment: The First Line of Defense
- 2. The Heart of the System: Reverse Osmosis Booster Pump
- 3. The RO Membrane and Separation
- 4. Storage and Distribution
- Benefits of Investing in a Commercial Reverse Osmosis System
- Unparalleled Water Quality
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
- Applications Across Industries
- Choosing the Right Commercial RO System: A Buyer's Guide
- 1. Water Source Analysis
- 2. Sizing and Capacity
- 3. Understanding Costs
- Installation, Operation & Essential Maintenance
- Installation Best Practices
- Routine Maintenance
- Emergency Considerations
- Advanced Considerations & Future Trends
- High Recovery & Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
- Smart Monitoring
- Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the best reverse osmosis water filtration system for a factory?
- Does reverse osmosis remove fluoride effectively?
- How often do I need to replace the membranes?
- Can I use a commercial RO system for well water?
- Do commercial RO systems remove microplastics?
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction: The Critical Role of Pure Water in Commercial Operations
In the modern industrial landscape, water is rarely just a utility; it is a critical ingredient, a cleaning agent, and a system component. From pharmaceutical manufacturing to boiler feed water, the quality of water directly impacts operational efficiency and product integrity. Industrial water treatment has therefore evolved from a luxury to a necessity. At the forefront of this technology is the commercial reverse osmosis system, a gold standard for filtration that ensures consistent, high-purity water.
This comprehensive guide provides a deep dive into commercial reverse osmosis (RO) technology for 2026. We will move beyond surface-level definitions to explore the engineering principles, detailed cost structures, and maintenance protocols required for optimal performance. Whether you are upgrading an existing facility or specifying a new reverse osmosis system for well water, this article equips you with the expertise to make data-driven decisions.
What is a Commercial Reverse Osmosis System?
The Science of Separation
At its core, reverse osmosis is a process that reverses the natural phenomenon of osmosis. In nature, osmosis involves water moving from a less concentrated solution to a more concentrated one through a semi-permeable membrane. As defined in encyclopedic sources like Wikipedia, reverse osmosis applies external pressure to the concentrated side (the contaminated water) to force water molecules through the membrane to the less concentrated side (the pure water), effectively leaving dissolved solids and contaminants behind.
Commercial vs. Residential Distinction
While the fundamental science remains the same, a commercial reverse osmosis system differs vastly from a residential unit. Residential systems are typically designed for low volume (50–100 gallons per day) and intermittent use. In contrast, commercial and industrial systems are engineered for high-capacity continuous operation, often processing thousands of gallons per day (GPD). They utilize larger, spiral-wound membranes, high-duty pumps, and sophisticated pre-treatment arrays to handle complex water chemistries.
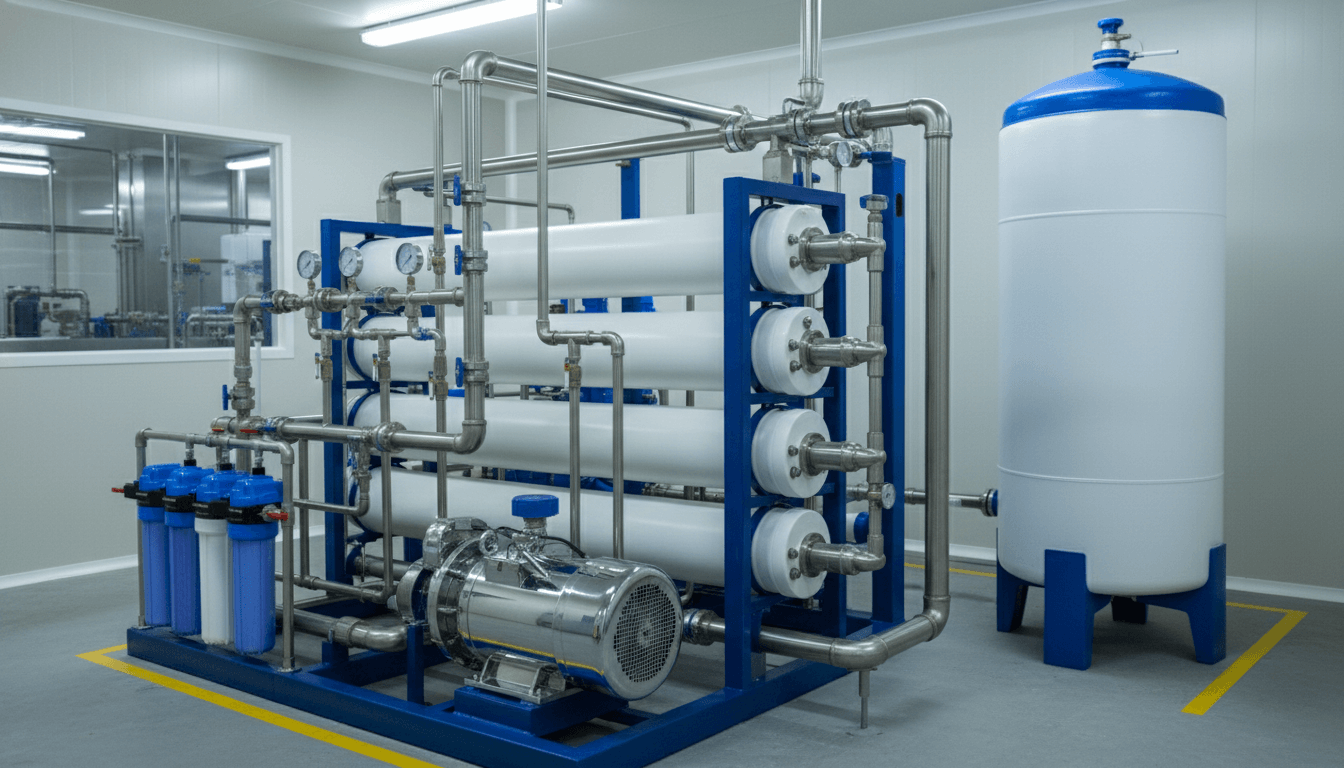
How Commercial Reverse Osmosis Systems Work: A Deep Dive
The efficacy of an RO system relies on a multi-stage process, where each component plays a vital role in protecting the membrane and ensuring purity.
1. Pre-Treatment: The First Line of Defense
Raw water often contains chlorine, sediment, and hardening minerals that can destroy RO membranes.
· Sediment Filters: Remove particulate matter to prevent physical clogging.
· Carbon Filtration: Essential for removing chlorine and chloramines, which can oxidize and degrade thin-film composite membranes.
· Water Softeners & Antiscalants: Hard water minerals (calcium and magnesium) cause scaling. For commercial applications, antiscalant dosing is often preferred over standard softening for cost-efficiency at high flow rates.
2. The Heart of the System: Reverse Osmosis Booster Pump
To overcome the natural osmotic pressure of the water—especially when treating water with high Total Dissolved Solids (TDS)—a powerful reverse osmosis booster pump is required. This pump generates the necessary pressure (typically 150–250 psi for brackish water) to force water molecules through the microscopic pores of the membrane.
3. The RO Membrane and Separation
Inside the pressure vessel, the feed water is split into two streams:
· Permeate: The purified water that passes through the membrane.
· Concentrate (Reject): The waste stream containing the concentrated contaminants.
Commercial systems often use "cross-flow" filtration, which allows the concentrate to sweep away contaminants from the membrane surface, reducing fouling.
4. Storage and Distribution
Unlike residential units that use a small bladder tank, commercial setups often require large atmospheric tanks. To deliver this stored water to the facility, a re-pressurization loop is needed. Alternatively, for smaller commercial applications, you might use a pressurize reverse osmosis storage tank to maintain line pressure without an additional delivery pump.
Benefits of Investing in a Commercial Reverse Osmosis System
Unparalleled Water Quality
Commercial RO systems are capable of removing up to 99% of dissolved salts, bacteria, and organics. For industries concerned with emerging contaminants, a common question is: does reverse osmosis remove fluoride? According to data from the CDC, reverse osmosis is highly effective at removing fluoride, along with arsenic, lead, and nitrates, making it ideal for food and beverage safety.
Additionally, with the rising concern over plastic pollution, a reverse osmosis water filter for microplastics is becoming a standard requirement. The pore size of an RO membrane is approximately 0.0001 microns, whereas microplastics are typically 5 millimeters down to 1 micron. This physical barrier effectively blocks virtually all microplastic particles.
Operational Efficiency and Cost Savings
High-quality water protects downstream equipment. Boilers and cooling towers fed with RO permeate experience significantly less scaling, reducing downtime and energy costs. In sectors like agriculture, consistent water quality ensures predictable crop yields.
This level of purification process is why a Reverse Osmosis Water Filter is essential for food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic production, ensuring that the final product meets stringent health and safety standards.
Applications Across Industries
|
Industry |
Application |
Critical Benefit |
|
Pharmaceuticals |
USP Grade Water production |
Removal of endotoxins and bacteria. |
|
Food & Beverage |
Ingredient water & bottling |
Consistent taste and removal of fluoride/chlorine. |
|
Manufacturing |
Boiler feed & cooling towers |
Prevention of scale and corrosion. |
|
Agriculture |
Hydroponics |
Precision nutrient control (removing background minerals). |
|
Hospitality |
Spot-free rinse & drinking water |
Enhanced guest experience and equipment protection. |
Choosing the Right Commercial RO System: A Buyer's Guide
Selecting the best reverse osmosis water filter system for commercial use involves more than just picking a flow rate. It requires a holistic analysis of your water source and facility needs.
1. Water Source Analysis
Are you treating municipal water or well water? A reverse osmosis system for well water typically requires more robust pre-treatment to handle iron, manganese, and varying biological loads compared to city water.
2. Sizing and Capacity
Accurately calculate your daily and peak hour demand. Oversizing increases initial reverse osmosis system cost, while undersizing leads to storage depletion and premature system wear.
3. Understanding Costs
A frequent inquiry is how much does a reverse osmosis system cost?
· Small Commercial (500–2,000 GPD): Typically ranges from $1,800 to $5,000.
· Mid-Sized (2,000–10,000 GPD): Can range from $8,000 to $20,000 depending on automation and pre-treatment.
· Industrial Large Scale: Custom systems often exceed $50,000.
Costs also depend on materials (stainless steel vs. PVC) and the inclusion of advanced features like variable frequency drives (VFDs).
Installation, Operation & Essential Maintenance
Installation Best Practices
Proper site preparation is crucial. Ensure adequate drainage for the concentrate stream and appropriate electrical power for the pumps. When installing a reverse osmosis tank, verify that the floor load capacity can support the weight of a full tank.
Routine Maintenance
Neglecting maintenance is the leading cause of system failure.
· Daily: Check pressure gauges and flow meters.
· Monthly: Test water quality (TDS in/out) to calculate rejection rates.
· Quarterly: Replace pre-filters.
· Annually: Sanitize the system.
Emergency Considerations
In critical sectors like healthcare or disaster relief, emergency reverse osmosis units are vital. These are often containerized or mobile systems designed to operate independently of the grid, ensuring a supply of potable water when municipal infrastructure fails.
Advanced Considerations & Future Trends
High Recovery & Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
Modern systems are pushing the boundaries of efficiency. High-recovery RO systems utilize innovative hydraulic designs to recycle concentrate, significantly reducing wastewater.
Smart Monitoring
IoT integration allows facility managers to monitor pressure drops and membrane health remotely, predicting maintenance needs before they become critical failures.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best reverse osmosis water filtration system for a factory?
The "best" system depends entirely on your feed water quality and volume needs. However, look for systems with non-proprietary components (like standard 4040 membranes) and robust frames (stainless steel or powder-coated aluminum) to ensure long-term serviceability.
Does reverse osmosis remove fluoride effectively?
Yes. As noted by the CDC, reverse osmosis is one of the most effective methods for removing fluoride from drinking water, typically achieving rejection rates of 90-95%.
How often do I need to replace the membranes?
In a commercial setting with proper pre-treatment, RO membranes can last 3 to 5 years. However, if you notice a permanent drop in flow or an increase in permeate TDS that cleaning cannot restore, replacement is necessary.
Can I use a commercial RO system for well water?
Absolutely. A reverse osmosis system for well water is highly effective but requires a detailed water analysis first. You must treat iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide before the water reaches the RO membrane to prevent rapid fouling.
Do commercial RO systems remove microplastics?
Yes. A reverse osmosis water filter for microplastics is extremely effective. The membrane's 0.0001-micron pore size is significantly smaller than microplastic particles, providing a reliable barrier against these emerging contaminants.
Conclusion
Investing in a commercial reverse osmosis system is a strategic decision that enhances product quality, protects equipment, and ensures compliance with environmental standards. By understanding the nuances of system selection—from the reverse osmosis booster pump to the storage configurations—you can secure a reliable water treatment solution for 2026 and beyond.
For businesses seeking robust and reliable solutions, Pure Water Reverse Osmosis Filter technologies play a critical role in achieving consistent, high-purity water output. YUANYANG’s Pure Water Reverse Osmosis Filter delivers top-tier industrial water purification designed to meet the rigorous demands of modern industry.
References
· Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Drinking Water Treatability Database
· National Institutes of Health (NIH): Removal of Microplastics by Water Treatment

Ultimate Storage Tank Guide for 2026: Selection & Innovations

Ultimate Guide to Filling Machine 2026 : Application & Selection

Emulsion Mixer Mastery: Industrial High-Performance Use

Ultimate Guide: Differences Between Homogenizer & Emulsifier

Why Your RO Systems Make Noise: Causes & Fixes
Medicine
How do you ensure the long-term stability of Yuanyang equipment?
Yuanyang’s equipment uses high-quality components and advanced technology, rigorously tested to ensure stable operation. We also provide comprehensive after-sales service and technical support to ensure the long-term stability of our equipment.
Automatic Screw Capping Machine
Can this capping machine for bottles be connected with filling machine,or labeling machine?
Yes, if client already has an old automatic labeling machine, just tell the conveyor height, we will customize our capping machine height.
Sachet Packaging Machine for Granules
What’s the sealing method of this type of sugar bag packing machine?
There are common 3 types of sealing method: back sealing, three sides sealing, four sides sealing.
Vacuum Emulsifier
What’s the brand of motor for this vacuum emulsifying mixer?
We have different brand of motor for clients to choose. The standard motor brand is Beide, optional choice is Siemens and ABB.
Liquid Soap Mixer
Can you also provide the related production machines?
Yes, we supply the complete set of liquid soap production machines, such as filling machine,capping machine,labeling machine,sealing machine, and coding machine.
Leave a message
Have any questions or concerns about our products? Please leave us a message here, and our team will get back to you promptly.






 Scan QR Code
Scan QR Code
Facebook
YouTube
LinkedIn
Whatsapp: +8613434139712
Guangzhou Yuanyang Machinery